MUST is a modal verb.
With modals verbs, there is only one form of it for every subject pronoun:
- I must
- You must
- He must
- She must
- It must
- We must
- They must
You see there is no change in the word MUST.
Just like the other modal verbs, there is never an S at the end of must:
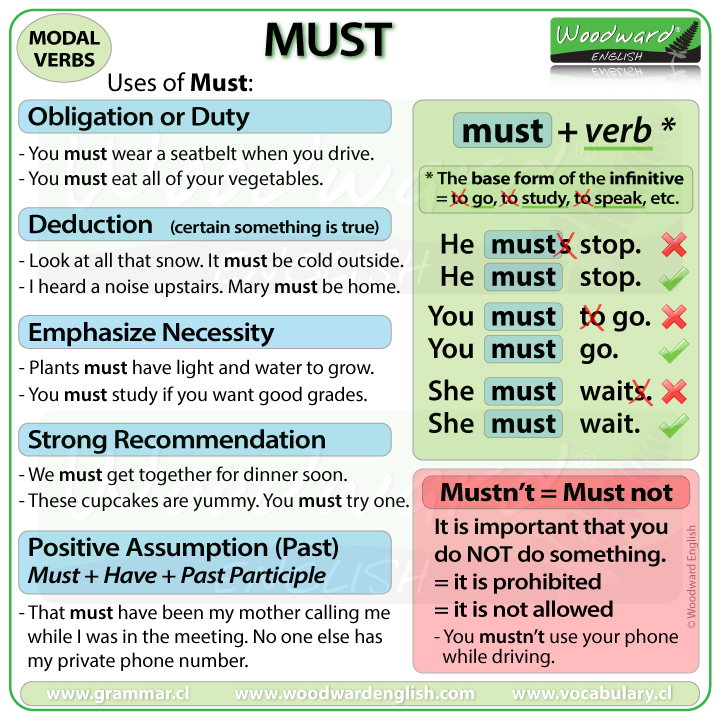
- He musts stop. (This is NOT CORRECT)
- He must stop. (This is CORRECT)
After Must we have the verb, or more specifically, the base form of the infinitive.
This means the infinitive without To. For example the infinitive is To Go so the base form is just the Go part.
Instead of To study, only study. Instead of To speak, we only put speak after the modal verb Must.
For example:
- You must to go.(This is NOT correct – we don’t use all of the infinitive – we need to remove the TO part)
- You must go. (Correct)
- He must waits.(This IS NOT correct – we don’t conjugate the verb so no S is necessary at the end – we need the base form of the infinitive)
- He must wait. (This is correct)
Some example sentences with Must are…
- I must study
- You must respect your parents.
- He must wear a helmet when he rides his bike.
- She must see a doctor before it becomes worse.
- It must be ready by tomorrow.
- We must listen to all of the instructions.
- They must follow the rules.
In what situations do we use MUST?
1. To express obligation or duty
MUST is used to express obligation or duty.
This also refers to complying with rules, laws and regulations.
If this obligation isn’t completed, then there will be problems or serious consequences.
- She must pass the English exam. She cannot graduate without it.
As a part of the regulations, she needs to pass the English exam before she can graduate. There is an obligation to pass.
- You must wear a seatbelt at all times.
This is the law so it is your obligation to wear one.
- You must eat all of your vegetables or you won’t get any dessert.
This is what the mother or father says to their child. It is an obligation and the child does not have a choice.
2. To emphasize the necessity of something
MUST is used to emphasize the necessity of something, that something is needed or necessary.
- Plants must have light and water to grow.
Light and water are needed or are necessary for the plant to grow.
- The road is very busy. You must look both ways before crossing it.
You need to do this, unless you want to get run over.
- You must study before the exam if you want to get a good grade.
Yes, study is always needed.
3. Deduction – Sure that something is true (Certainty)
Must is used when you are sure or certain that something is true based on evidence.
It can be used when we don’t know something exactly but we are very certain that it is true.
- Look at all of that snow. It must be really cold outside.
I’m sure or certain that it is cold outside (based on the evidence of all the snow out there… and snow is cold)
- Mary must be home. I heard a noise coming from her room.
I’m sure it is Mary because she is usually home from school at this time of day.
- It’s five in the morning and you still haven’t gone to bed? You must be tired!
I’m certain you are tired because I would be tired too if I hadn’t slept all night.
4. Expresses positive logical assumptions about the past (Must + have + past participle)
Must can also be used when making positive assumptions, using logic, about things that happened in the past. For this we use Must + have + the past participle
- That must have been my mother calling me while I was in the meeting. Nobody else has my private number.
That is my logical assumption about what happened in the past, someone calling me.
- He must have won the lottery with the new house and car he has just bought.
I can’t think of any other way he would suddenly have so much money so my logical assumption is that he must have won the lottery.
5. A strong recommendation (or strong advice)
Must can also used as a strong recommendation or as strong advice.
It means that something is highly recommended (stronger than using should)
- The cupcakes here are delicious. You must try one.
Yes, I highly recommend it.
- You must see the new Joe Jackson movie, it’s fantastic.
It is my advice … my strong recommendation.
- You must get that strange mole checked out by a dermatologist.
As you can see, all of these examples are strong recommendations and are highly recommended by you.
MUST NOT – MUSTN’T
The negative of Must is Mustn’t
Mustn’t is a contraction, or short way of saying Must not.
Mustn’t is a negative obligation. It is important that you do NOT do something.
In a way, mustn’t is the same as saying it is prohibited or it is not allowed.
Mustn’t = Do not do this! You don’t have a choice.
Let’s look at some examples sentences with mustn’t.
- You mustn’t use your phone while you are driving.
Yes, it is prohibited to use your phone while driving as you will be distracted and may cause an accident.
- Students mustn’t talk during the exam.
Talking is not allowed during the exam.
- You must not open the gift until your birthday.
This means you must wait. You are not allowed to open the gift before then.
- You mustn’t tell Susan. It’s a surprise for her.
Yes, it is important that you do NOT tell Susan or it will ruin the surprise.
MUST Summary Chart