SO – TOO – English Grammar Lesson
- Person A: I am happy.
- Person B: I am happy too.
Too is used to show agreement with a positive statement.
Too appears at the END of a sentence.
Too means also.
I am happy too. = I am also happy.
Too can also mean in a similar way.
I am happy in a similar way.
But if someone says: I am happy.
and you say: I am happy too.
It is possible, it is correct BUT it also sounds repetitive.
It is more common to use the word SO.
For example: So am I.
So am I. = I am happy too.
Notice the word order: SO + Auxiliary + Subject
SO + Auxiliary + Subject
The auxiliary verb needs to agree with the verb tense in the original statement or sentence.
In the first sentence “I am happy.” The verb is am which is a form of To Be in the present simple tense.
If the verb is in the present simple tense in the first sentence, then the response is in the same tense (the present simple tense) which becomes … So AM I.
Let’s look at a similar example:
- I was happy.
What tense is used here?
The past simple tense.
Since we have to use the same tense… what would the girl’s response be?
- So was I.
Both sentences are in the past simple tense.
- Person A: I was happy.
- Person B: So was I.
What happens if you are talking about other people?
The same concept applies.
Here, the man in the middle is not saying: I am happy.
No, he is pointing at the boy.
So, he is going to say:
- He is happy.
The other boy in the middle could say “So am I” if he is talking about himself.
BUT in the picture in the video, the boy is pointing at the girl on the right.
In this case, the boy would say:
- So is she.
The first sentence is the present simple tense, so the response will also be in the present simple tense.
And if they are talking about the past. The sentences would be:
- Person A: He was happy.
- Person B: So was she.
Both are in the past simple tense.
Now, all of these sentences have used TO BE… in the present simple and past simple tense.
What happens with other tenses?
Look at this sentence:
- I need more money.
This sentence is in the present simple tense which means the response also needs to be in the present simple tense. However, it is not TO BE. It has the verb NEED.
Do we respond with: So need I ? NO!
We do NOT respond with the same verb we need to use an auxiliary verb.
We say:
- So do I.
The auxiliary verb for the present simple tense is Do or Does.
In this case we used DO because the subject is I …. So do I.
So the complete interaction is:
- Person A: I need more money.
- Person B: So do I.
We use an auxiliary for all verbs except for TO BE and Modal verbs.
Let’s look at the same sentence in the past tense.
- I needed more money.
Needed is in the past simple tense. This means we need a past simple tense auxiliary verb.
How can we respond?
- So did I.
DID is the past simple tense auxiliary verb.
So the complete interaction is:
- Person A: I needed more money.
- Person B: So did I.
Let’s look at more ways of responding.
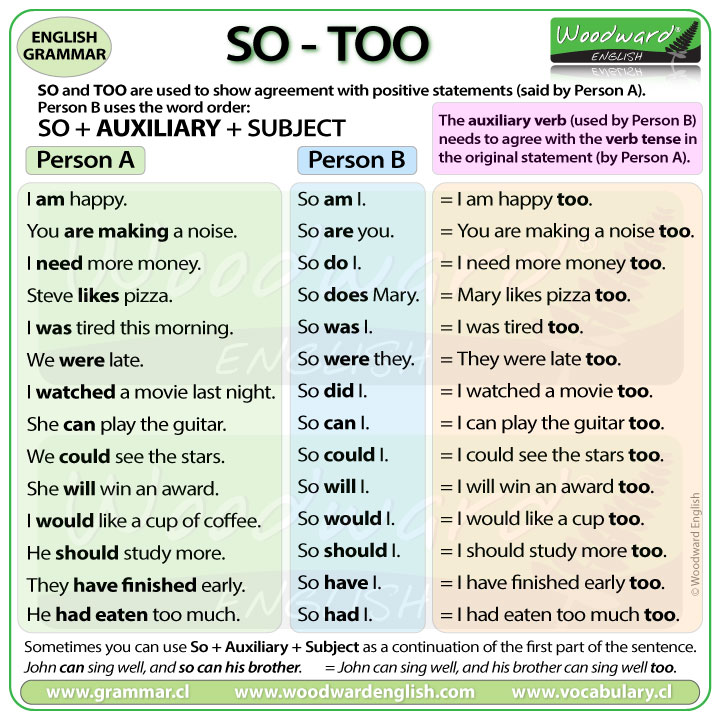
SO and TOO are used to show agreement with positive statements said by person A.
Person B uses the word order: SO + AUXILIARY + SUBJECT.
The auxiliary verb used (by person B) needs to agree with the verb tense in the original statement (by Person A).
Look at these examples:
SO with the Present Tense
- Person A: I am happy.
Person B needs to use the same tense so would respond with:
- So am I.
So am I = I am happy too.
- You are making a noise.
The response could be:
- So are you. = You are making a noise too!
As we have already seen:
- I need more money.
- So do I. = I need more money too.
Let’s try this a little differently:
- Steve likes Pizza.
You could say: So do I … but let’s talk about another person liking pizza too, let’s use the name Mary. The response would be:
- So does Mary.
DOES because the auxiliary DOES is used for he/she/it.
When I say: So does Mary, it means Mary likes pizza too.
SO with the Past Tense
- I was tired this morning.
This is the past simple tense of To Be so we need to respond with the same tense.
- So was I.
So was I. = I was tired too.
With the other form of To Be in the past simple tense…
- We were late.
Again we need to use the same past tense in the response. This time let’s use THEY in our response. It becomes…
- So were they.
So were they. = They were late too.
- I watched a movie last night.
This is the past simple tense and it is NOT to be. The main verb is watched.
This means we need to use the past tense auxiliary DID, so the response could be:
- So did I.
This means: I watched a movie last night too.
So let’s quickly go through each of these again:
- Person A: I am happy.
Person B: So am I. - Person A: You are making a noise.
Person B: So are you. - Person A: I need more money.
Person B: So do I. - Person A: Steve likes pizza.
Person B: So does Mary. - Person A: I was tired this morning.
Person B: So was I. - Person A: We were late.
Person B: So were they. - Person A: I watched a movie last night.
Person B: So did I.
Let’s see some more examples with some modal verbs and perfect tenses.
SO with Modal Verbs
- She can play the guitar.
This has the modal verb CAN, so we use the same modal verb in the response.
- So can I.
This means: I can play the guitar too.
- We could see the stars.
If the first past has the modal verb could, then the response needs the same.
- So could I.
This means: I could see the stars too.
- She will win an award.
Here it uses WILL to talk about the future, so our response needs to use WILL too.
- So will I.
This means: I will win an award too.
- I would like a cup of coffee.
If the first statement has WOULD, our response needs WOULD.
- So would I.
This means: I would like a cup of coffee too.
- He should study more.
The modal verb SHOULD is used. We need to use the same in the response.
- So should I.
This means I should study more too.
SO with Perfect Tenses
- They have finished early.
Here we have the present perfect tense. In this case we use the auxiliary verb HAVE in our response.
- So have I.
This means: I have finished early too.
- He had eaten too much.
This is another perfect tense, this time the past perfect tense so we need to use the same auxiliary (HAD) in our response.
- So had I.
This means: I had eaten too much too.
So let’s quickly go through each of these again:
- Person A: She can play the guitar.
Person B: So can I. - Person A: We could see the stars.
Person B: So could I. - Person A: She will win an award.
Person B: So will I. - Person A: I would like a cup of coffee.
Person B: So would I. - Person A: He should study more.
Person B: So should I. - Person A: They have finished early.
Person B: So have I. - Person A: He had eaten too much.
Person B: So had I.
More than a response
SO isn’t only used in a response.
Sometimes we can use: SO + AUXILIARY + SUBJECT as a continuation of the first part of the sentence.
For example:
- John can sing well, and so can his brother.
This is the same as saying:
- John can sing well and his brother can sing well too.
We use the first sentence so that you don’t sound repetitive.
Summary Chart
Videos lessons about TOO
You may be interested in the following videos about TOO:
